Intermediate result from partners RTR, SISW, ULille, UTCN , VUB, TUV
This result has been achieved on 30 November 2020 in month 24 of the project.
To build a virtual test it is necessary to have data and scenarios from real tests in order to have comparable results. RTR performed tests on a Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) Renault Zoe according to the demands from PANDA partners. The tests results were compared with simulation results developed by PANDA partners and an analysis of the simulations was done. With data and scenarios form real tests there were build virtual tests for the same BEV using EMR proposed simulation architecture.
- Objectives:
- To build virtual tests for a BEV with results close to real tests.
- To validate the models developed and to prove the efficiency and flexibility of the proposed simulation architecture.
- Resesarch: Real tests were performed by RTR according to test conditions demands: temperature, distance, different scenarios etc. Test results are compared with simulation results done by SISW by using models developed by VUB, UTCN, ULille. A detailed analysis of simulation results and test measurements was done.
- Results:
- Measurement data from real BEV in different use cases of the vehicle.
- Different simulation architectures built according to the EMR formalism were validated
- Precision and flexibility of the proposed multi-level simulations were demonstrated.
- An LCA study has been proposed on the climate change indicator
- What will it be used for: The validated simulation models will be used for next step of the project, real time simulations.
- Impact: Precision and flexibility of the proposed multi-level simulations can lead to reduce the time to market for electrified vehicles as they can replace some real tests.

Figure 1: Renault ZOE – BEV used
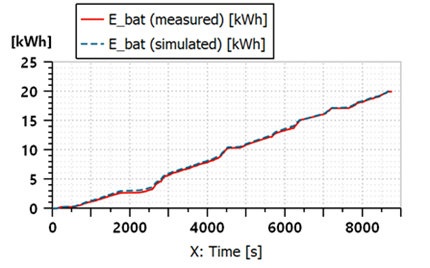
Figure 2: Energy consumption form the battery during the test (comparison virtual vs real test results)